Error and bias in the STSDAS fitting package
I. Busko
STScI
Session ID: P5.11 Type: poster
Abstract:
The fitting package in STSDAS (Space Telescope Science Data
Analysis System) relies on two techniques for fitting functions to
data:
-
Linear functions (Legendre and Chebyshev polynomials, cubic
splines) are fitted by minimizing
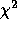 solving the normal
equations by the Cholesky method. Function coefficient errors are
computed directly from the covariance matrix. This technique is
provided by the IRAF (Image Reduction and Analsys Facility) library
curfit.
solving the normal
equations by the Cholesky method. Function coefficient errors are
computed directly from the covariance matrix. This technique is
provided by the IRAF (Image Reduction and Analsys Facility) library
curfit.
-
Any function, linear or non-linear in its coefficients, can
be fitted by minimizing
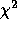 using the downhill simplex
method, also known as amoeba. This method is unable by design
to compute coefficient errors, thus the package relies on an independent
technique (bootstrap resampling) to estimate these errors.
using the downhill simplex
method, also known as amoeba. This method is unable by design
to compute coefficient errors, thus the package relies on an independent
technique (bootstrap resampling) to estimate these errors.
In this work, the reliability of both coefficient and their error bars
computation by both of the bove methods was assessed by using simulated
data in a Monte Carlo approach.
The goal was to detect and estimate the magnitude of possible
systematic deviations of the computed coefficients from the ``true'' ones.
Computed error bars were also compared with the coefficient underlying
parent population's standard deviation in order to measure any systematic
over or under-estimation in the error barrs.
It was found that both methods can generate slightly biased coefficients
(at the 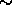 few percent level) and over or under-estimated error bars
(at the
few percent level) and over or under-estimated error bars
(at the 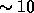 percent level), in particular in low
signal-to-noise data.
percent level), in particular in low
signal-to-noise data.
Patrick P. Murphy
Wed Sep 11 13:10:49 EDT 1996