Faraday Rotation



Next: TECHNICAL ISSUES AND
Up: OBJECTS AT HIGH
Previous: Starbursts at High
Recently, two radio galaxies with 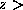 3 have been shown to have
large Faraday rotation in their rest frame. The magnitude of the
rotation measure is similar to that in nearby cooling flow clusters.
These radio galaxies may be located in the centers of similar dense
clusters, or the environments of more isolated systems at high
redshift may enveloped in a strong magnetic field. Current arguments
suggest that very massive clusters would not have formed at such high
redshifts, so the second possibility may be favored. In this case,
magnetic fields may play an important part in galaxy formation.
3 have been shown to have
large Faraday rotation in their rest frame. The magnitude of the
rotation measure is similar to that in nearby cooling flow clusters.
These radio galaxies may be located in the centers of similar dense
clusters, or the environments of more isolated systems at high
redshift may enveloped in a strong magnetic field. Current arguments
suggest that very massive clusters would not have formed at such high
redshifts, so the second possibility may be favored. In this case,
magnetic fields may play an important part in galaxy formation.
Our study of this phenomena is limited by the decrease in the rest
frame Faraday rotation by 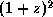 . The 2.4 GHz band is important to
provide the frequency coverage to measure the reduced rotation
measures. Sensitivity is important because of the low net
polarizations from these sources. Resolution plus sensitivity is also
critical to prevent the change in rotation measure across these
sources from canceling out the polarization signal. Of course, the
more resolution we have the more we can learn about the geometry of
these fields. Thus once again polarization and the upgrade are
important to studies of magnetic fields in high-z objects.
. The 2.4 GHz band is important to
provide the frequency coverage to measure the reduced rotation
measures. Sensitivity is important because of the low net
polarizations from these sources. Resolution plus sensitivity is also
critical to prevent the change in rotation measure across these
sources from canceling out the polarization signal. Of course, the
more resolution we have the more we can learn about the geometry of
these fields. Thus once again polarization and the upgrade are
important to studies of magnetic fields in high-z objects.
newvla@nrao.edu
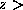 3 have been shown to have
large Faraday rotation in their rest frame. The magnitude of the
rotation measure is similar to that in nearby cooling flow clusters.
These radio galaxies may be located in the centers of similar dense
clusters, or the environments of more isolated systems at high
redshift may enveloped in a strong magnetic field. Current arguments
suggest that very massive clusters would not have formed at such high
redshifts, so the second possibility may be favored. In this case,
magnetic fields may play an important part in galaxy formation.
3 have been shown to have
large Faraday rotation in their rest frame. The magnitude of the
rotation measure is similar to that in nearby cooling flow clusters.
These radio galaxies may be located in the centers of similar dense
clusters, or the environments of more isolated systems at high
redshift may enveloped in a strong magnetic field. Current arguments
suggest that very massive clusters would not have formed at such high
redshifts, so the second possibility may be favored. In this case,
magnetic fields may play an important part in galaxy formation.
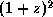 . The 2.4 GHz band is important to
provide the frequency coverage to measure the reduced rotation
measures. Sensitivity is important because of the low net
polarizations from these sources. Resolution plus sensitivity is also
critical to prevent the change in rotation measure across these
sources from canceling out the polarization signal. Of course, the
more resolution we have the more we can learn about the geometry of
these fields. Thus once again polarization and the upgrade are
important to studies of magnetic fields in high-z objects.
. The 2.4 GHz band is important to
provide the frequency coverage to measure the reduced rotation
measures. Sensitivity is important because of the low net
polarizations from these sources. Resolution plus sensitivity is also
critical to prevent the change in rotation measure across these
sources from canceling out the polarization signal. Of course, the
more resolution we have the more we can learn about the geometry of
these fields. Thus once again polarization and the upgrade are
important to studies of magnetic fields in high-z objects.