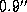 for Europa to
for Europa to 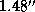 for Ganymede, and Titan's
diameter never exceeds
for Ganymede, and Titan's
diameter never exceeds 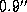 . These objects occupy in central
position in planetary science, exhibiting a wide range of interesting
physical phenomena from hot spots with volcanos on Io to a complex
atmosphere more dense than Earth's on Titan. Disk averaged brightness
temperatures of these objects have been measured with the VLA and
Titan has been extensively studied with the VLA/Goldstone radar
configuration, again with essentially full-disk averaging. The
enhanced VLA will significantly advance the study of these objects in
two important ways. Io and Europa's orbits are very close the surface
of Jupiter and confusion from the planet severely affects the
measurements of the satellites' disk temperatures as a function of
their orbital longitudes. Jupiter's confusing flux density can be
minimized by greatly increasing the continuum bandwidth of the
VLA. Continuum observations of Io at
. These objects occupy in central
position in planetary science, exhibiting a wide range of interesting
physical phenomena from hot spots with volcanos on Io to a complex
atmosphere more dense than Earth's on Titan. Disk averaged brightness
temperatures of these objects have been measured with the VLA and
Titan has been extensively studied with the VLA/Goldstone radar
configuration, again with essentially full-disk averaging. The
enhanced VLA will significantly advance the study of these objects in
two important ways. Io and Europa's orbits are very close the surface
of Jupiter and confusion from the planet severely affects the
measurements of the satellites' disk temperatures as a function of
their orbital longitudes. Jupiter's confusing flux density can be
minimized by greatly increasing the continuum bandwidth of the
VLA. Continuum observations of Io at 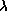 7mm and
7mm and 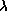 1.3cm
should then reveal the variations in mean surface brightness caused by
the changes in the viewing geometry as Io orbits Jupiter. The hot
spots have been observed only in the IR which is sensitive to the very
surface. Measurements at
1.3cm
should then reveal the variations in mean surface brightness caused by
the changes in the viewing geometry as Io orbits Jupiter. The hot
spots have been observed only in the IR which is sensitive to the very
surface. Measurements at 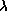 7mm and
7mm and 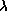 1.3cm will probe
the hot spots to depths of roughly 10 wavelengths. The subsurface
probing is important for all of the satellites. The improvement in
sensitivity at
1.3cm will probe
the hot spots to depths of roughly 10 wavelengths. The subsurface
probing is important for all of the satellites. The improvement in
sensitivity at 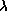 1.3cm as well as full capability in the 40-50
GHz band are very important for these measurements.
1.3cm as well as full capability in the 40-50
GHz band are very important for these measurements.