



Next: The Clark algorithm
Up: The `CLEAN' algorithm
Previous: The `CLEAN' algorithm
This algorithm proceeds as follows:
- Find the strength and position of the peak (i.e., of the greatest
absolute intensity) in the dirty image
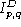 .
.
- Subtract from the dirty image, at the position of the peak, the
dirty beam
B multiplied by the peak strength and a damping factor
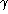 (
( 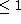 , usually termed the loop gain).
, usually termed the loop gain).
- Go to (1) unless any remaining peak is below some user-specified
level. The search for peaks may be constrained to specified
areas of the image, called `CLEAN' windows.
- Convolve the accumulated point source model
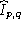 with an
idealized `CLEAN' beam
(usually an elliptical Gaussian fitted to the central lobe of the dirty
beam).
with an
idealized `CLEAN' beam
(usually an elliptical Gaussian fitted to the central lobe of the dirty
beam).
- Add the residuals of the dirty image to the `CLEAN'
image.
The fifth step is sometimes omitted, but it is recommended because it
can provide useful diagnostic information about the noise on the
image, residual sidelobes, ``bowls'' near the image center (see
the problem of short spacings).




Next: The Clark algorithm
Up: The `CLEAN' algorithm
Previous: The `CLEAN' algorithm

1996 November 4
10:52:31 EST
