


Next: Description of Infrared Water
Up: An Infrared Water Vapour
Previous: An Infrared Water Vapour
- Operates near the peak of the Planck function for atmospheric
temperatures
- Wavelength range carefully selected to include only
transitions from water vapour
- Wavelength range includes mixture of strong and weak lines and
therefore samples different heights, in effect yielding an average
over whole atmosphere
- Theoretical atmospheric model supported by FTS measurements
from Mauna Kea (Naylor et. al. PASP 96, 167 (1984)). Inputs are base
pressure and temperature.
- IWVM sensitivity (expressed in terms of
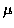 m pwv)
improves as the pwv decreases
(Fig 1).
For example, if the IWVM
can detect variations of
m pwv)
improves as the pwv decreases
(Fig 1).
For example, if the IWVM
can detect variations of 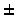 1
1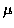 m pwv in a given integration
time when the
atmosphere contains 1mm pwv, it will detect variations of
m pwv in a given integration
time when the
atmosphere contains 1mm pwv, it will detect variations of
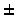 0.7
0.7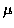 m and
m and 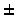 1.85
1.85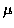 m when the atmosphere contains
0.5 and 3mm pwv respectively
m when the atmosphere contains
0.5 and 3mm pwv respectively
- Photoconductive detectors are simple devices offering high
speed, sensitivity and stability
- Diffraction limit at these wavelengths allows use of smaller
optics
- Design makes calibration intrinsically clean since optical
train is identical in all observing modes



Next: Description of Infrared Water
Up: An Infrared Water Vapour
Previous: An Infrared Water Vapour
Al Wootten
2000-04-04